About DBeaver DBeaver is a universal database management tool for everyone who needs to work with data in a professional way. With DBeaver you are able to manipulate with your data like in a regular spreadsheet, create analytical reports based on records from different data storages, export information in an appropriate format.
Update: August 12, 2018
Using a database in Python relies on being able to write database queries in SQL. In fact, a good way to test your Python scripts is to first test the SQL commands in a third-party program such as DBeaver. A good place you can currently live practice these skills is SQLZOO. In this tutorial i have described the process to connect DBeaver Sql Client With Derby DataBase.#DBeaverSQLClient. Create a folder to be used as your CSV Database. Mkdir /desktop/csvs. Place the CSV you want to. MacOS DMG – just run it and drag-n-drop DBeaver into Applications. Debian package – run sudo dpkg -i dbeaver.deb. Then execute 'dbeaver &'. RPM package – run sudo rpm.
The following post demonstrates how to import CSVs using Dbeaver's database to database export & import feature. If you are certain of the quality of your CSV & just want to import it quickly my subsequent post may be more useful.
0) Install DBeaver
You can find installation instructions here
1) Create a folder to be used as your CSV Database
mkdir ~/desktop/csvs

Place the CSV you want to load into this folder
2) Create a CSV database connection
In the menu bar select Database > Create a New Connection & from the list of drivers select Flat files(CSV) > CSV/DBF
Dbeaver Python Tutorial
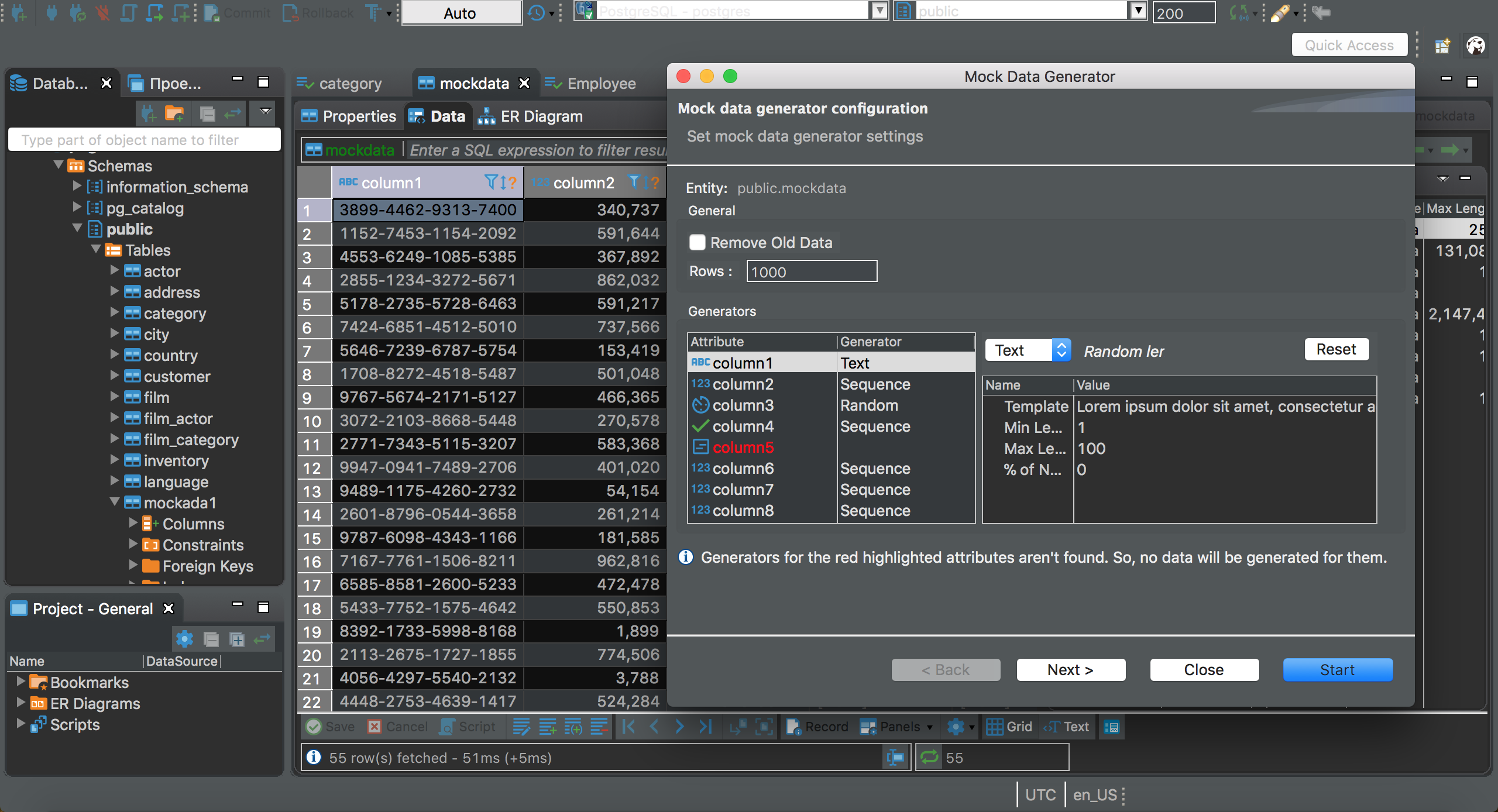
Set the path of the connection to the folder you created earlier (the JDBC URL will auto-populate)
Note: If you run into trouble downloading the driver navigate to the source website and download the driver manually

3) Connect to your target database
3.1) Navigate through your target database & schema and right click on your target table and select import table data
3.2) Next select your source CSV from your CSV connection as the source container
Note: In this example case I'm loading a test CSV into a Postgres database but this functionality works with any connection that DBeaver supports (which is basically everything)
4) Ensure that the mappings of each of your columns is correct
- For column names that are an exact match DBeaver will automatically map them for you
- For the remaining columns make sure to map the source columns to your desired target columns
Place the CSV you want to load into this folder
2) Create a CSV database connection
In the menu bar select Database > Create a New Connection & from the list of drivers select Flat files(CSV) > CSV/DBF
Dbeaver Python Tutorial
Set the path of the connection to the folder you created earlier (the JDBC URL will auto-populate)
Note: If you run into trouble downloading the driver navigate to the source website and download the driver manually
3) Connect to your target database
3.1) Navigate through your target database & schema and right click on your target table and select import table data
3.2) Next select your source CSV from your CSV connection as the source container
Note: In this example case I'm loading a test CSV into a Postgres database but this functionality works with any connection that DBeaver supports (which is basically everything)
4) Ensure that the mappings of each of your columns is correct
- For column names that are an exact match DBeaver will automatically map them for you
- For the remaining columns make sure to map the source columns to your desired target columns
5) Complete the wizard and watch DBeaver import your data
Note: For large files it may be necessary to go get lunch but in my case 4 records doesn't take long to import :)
6) Check to make sure that the data has loaded correctly
Dbeaver Python
As a last optional step it is good practice to make sure that everything loaded correctly which can easily be done by running a query against your target DB
7) Final Notes & Thoughts
- While this process takes a little bit more time to get setup than other tools setting up the CSV connection only needs to be done once
- One side benefit of this as well is that you are now able to run SQL queries against CSVs very easily
- The only real pain point that I have run across is that if you add a new CSV file or add/delete columns in an active CSV connection you have to cancel the import wizard & refresh the CSV connection for the changes to be picked up
- this feedback was provided in issue 926 and hopefully it will be resolved in a future update
Related
- Dark theme support was improved (Windows 10 and GTk)
- Data viewer:
- Copy As: format configuration editor was added
- Extra configuration for filter dialog (performance)
- Sort by column as fixed (for small fetch sizes)
- Case-insensitive filters support was added
- Plaintext view now support top/bottom dividers
- Data editor was fixed (when column name conflicts with alias name)
- Duplicate row(s) command was fixed for multiple selected rows
- Edit sub-menu was returned to the context menu
- Columns auto-size configuration was added
- Dictionary viewer was fixed (for read-only connections)
- Current/selected row highlighting support was added (configurable)
- Metadata search now supports search in comments
- GIS/Spatial:
- Map position preserve after tiles change
- Support of geometries with Z and M coordinates was added
- Postgis: DDL for 3D geometry columns was fixed
- Presto + MySQL geometry type support was added
- BigQuery now supports spatial data viewer
- Binary geo json support was improved
- Geometry export was fixed (SRID parameter)
- Tiles definition editor was fixed (multi-line definitions + formatting)
- SQL editor:
- Auto-completion for objects names with spaces inside was fixed
- Database objects hyperlinks rendering was fixed
- SQL Server: MFA (multi-factor authentication) support was added
- PostgreSQL: array data types read was fixed
- Oracle: indexes were added to table DDL
- Vertica: LIMIT clause support was improved
- Athena: extra AWS regions added to connection dialog
- Sybase IQ: server version detection was improved
- SAP ASE: user function loading was fixed
- Informix: cross-database metadata read was fixed
- We migrated to Eclipse 2021-03 platform

